the load appled in c-scale of rockwell hardness test is|rockwell hardness test distance : manufacturer The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation . 11 de fev. de 2022 · Learn about some of the biggestMoney Mafias of the country who've been a part ofsome of the greatest money laundering cases. 🤑Catch Money Mafia, Monday nigh.
{plog:ftitle_list}
4 de ago. de 2021 · From CAs, and advocates, to villagers, 1 out of every 2 Indians has been a victim of identity theft. But who are the people behind this fraud, and how did they .
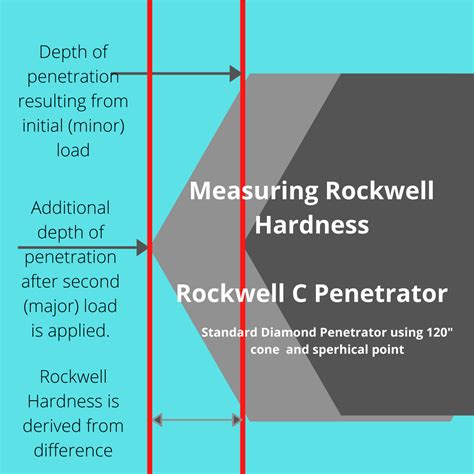
One regular Rockwell number represents a penetration of 0.002 mm (0.000080 inch). Therefore, a reading of C60 indicates penetration from minor to major load of (100 to 60 Rockwell points) x 0.002 mm = 0.080 mm or 0.0032 inch.

In this test method, the minor (preload) is always 3 kgf. The major load may be any of the following loads: 15kgf, 30 kgf, or 45 kgf. ASTM E18 contains a listing of all regular Rockwell scales and typical materials for which these scales are .Preliminary test loads (preloads) range from 3 kgf (used in the “Superficial” Rockwell scale) to 10 kgf (used in the “Regular” Rockwell scale). Total test forces range from 15kgf to 150 kgf (superficial and regular) to 500 to 3000 kgf . The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation .The deeper a defined indenter penetrates the surface of a specimen with a specified test load, the softer the material that is being tested. The Rockwell hardness (HR) is then determined from the residual indentation depth, along .
The Rockwell test is particularly suitable for measuring the hardness of hardened metals and alloys. These materials often have high hardness levels and require higher applied loads to .Test Method Illustration. A = Depth reached by indenter after application of preload (small load). B = Position of indenter during total load, small plus large load. C = Final position reached by indenter after elastic recovery of sample .
Following are the steps included in Rockwell testing: 1. The indenter moves down into position on the part surface. 2. A minor load is applied and a zero reference position is established. 3. The major load is applied for .There are two general classes of Rockwell test: Rockwell and superficial Rockwell. In Rockwell testing, the minor load is 10 kgf and the major load is 60, 100 or 150 kgf. In.
The various indenter varieties and range of test loads form a matrix of Rockwell hardness scales, which can be applied to a wide range of materials. Every Rockwell hardness scale is identified by a letter signifying .
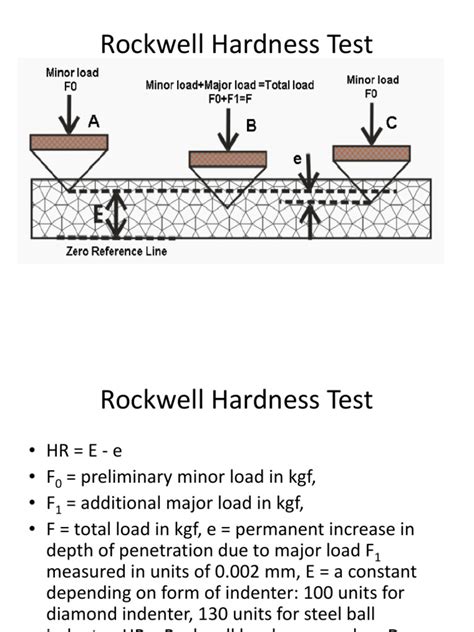
Definition of the Rockwell hardness test method The Rockwell hardness test methods are described by a number of scales, characterized by a standard, an indenter type, and a load. Examples of Rockwell hardness test methods: . Hardness Testing Loads. The hardness testing load is the load (“force”) that is applied to the indenter when pressing into the material being tested. The depth or size of the deformation made by the indenter will depend .This first load is removed, and another heavier load is applied to the indenter on the test piece. The Rockwell hardness of the test piece is calculated by subtracting the second load from the first and using the Rockwell formula. The resulting value is then translated to the Rockwell C scale of hardness to determine the hardness of the material.
The article helps you understand principle and applications of the Rockwell hardness test method. + 86 755 61301520; [email protected] . and the combination of initial minor loads and final major loads also distinguishes the Rockwell method from other test methods. The applied load ranges from 15kgf to 150kgf, where a 3kgf is usually .Scale C (carbide) testers are used for testing cemented carbides in the Rockwell A Scale, where tolerances of ± 0.20 of a Rockwell Hardness point are required. A specially selected “A” Brale penetrator is used to measure the hardness of cemented carbides in accordance with ASTM B 294 and the Cemented Carbide Producer’s Association (CCPA).A widely used variant of the Rockwell hardness test is the superficial Rockwell test, wherein the minor load is 3 N and the major loads are 15, 30, or 45 N.Further details on the Rockwell superficial hardness scales are available in the relevant ASTM standards (ASTM 1984).The Rockwell hardness values are expressed as a combination of hardness number and a scale . The minor load of 10 KGS is applied first. Remove the major load turning the handwheel back until the indicator hand is in position “set” on the dial. . The equation for the Rockwell hardness test for metals is below: d=depth from zero load point. N and s = various scale factors that can be found in the chart below. Rockwell A scale. Used .
Regular Rockwell Hardness Test where the minor load is 10 kgf and major load is 60, 100, or 150 kgf. Superficial Rockwell Hardness Test where the applied minor load is 3 kgf and the major loads are 15, 30, or 45 kgf. There are two types of Rockwell test (Table 23.1): Rockwell: the minor load is 10 kgf, the major load is 60, 100, or 150 kgf. Superficial Rockwell: the minor load is 3 kgf and major loads are 15, 30, or 45 kgf. Table 23.1: Some common scales in Rockwell and Superficial Rockwell testingExplanation: Most widely used hardness test is a Rockwell test in the US. It is because of the fast speed. It gives a small indentation. 2. Rockwell test utilizes _____ a measure of hardness. . Hardened steel is a very hard material. So it is tested by the diamond indenter. On C scale, the load of 150 kg is applied. advertisement. 8. Which .The Rockwell hardness scale is designed to determine the hardness of materials like aluminum, thin steel, lead, iron, titanium, copper alloys, and cemented carbides. . This is called as an indent and its depth is measured. The total test force is applied in two stages to eliminate errors caused due to the roughness of the surface and .
Hardness testing within the realm of materials testing. Today, hardness testing is one of the most widely used methods in mechanical materials testing, especially for metals. On the one hand, this test method can be used to find qualitative relations to other material properties (e.g., strength, stiffness, density) or to the material behavior under certain stresses (e.g., abrasion .Load: The Rockwell hardness test uses a pre-load of 10 kgf, followed by the application of the main load, which varies depending on the Rockwell scale being used (e.g., 60 kgf for the Rockwell A scale, 150 kgf for the Rockwell C scale). The load is .
Variants on the Rockwell hardness test procedure are used depending on the material and strength of a part. The most common Rockwell variants include: . HRC – Known as “Rockwell C,” a 150 kgf load is applied via a diamond in this method. . They also state the correct scale and call out the correct load and testing medium to be used. Brinell hardness test is an indentation hardness test.It uses a hard spherical ball (usually around 10mm in diameter). An applied force (a typical test will use 3,000 kilograms) pushes the ball against the surface of the .Hardness Testing. G. Sundararajan, M. Roy, in Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, 2001 1 Macrohardness Testing 1.1 Rockwell Hardness Testing. In a Rockwell hardness test, initially a minor load of 10 N is applied and the zero datum position is established.The major load (60, 100, or 150 N) is then applied for a specific period (a few .mechanism to ensure that the load is applied gradually. 7. As soon as the pointer comes to rest pull the handle in the reverse . Applications of Rockwell Hardness A ± Scale, B-Scale, C-Scale. 3. Type of Indentor used in the Three Different Scales of Rockwell Hardness . Selection of Load in Rockwell Hardness Test. AUROR $¶67(&+12/2*,&$/ .
At first, a preliminary test force (preload or minor load) is applied upon the sample with the help of a diamond or ball indenter. This preload breaks through the surface to decrease the effects of surface finish. . Additionally, metals have A, B, C, and F as the popular Rockwell hardness scales, while polymers use M and R scales. Superficial .
rockwell test loads explained
This happens under a large load compared to the indentation made by a pre-load. Different scales use varied loads or indenters such as: diamond tips, steel, or; tungsten carbide balls. . The Rockwell M hardness test is not valid for plastics that are less than 0.05 inch (1.27 mm) thick. This is because the indenter can penetrate too deeply .International Standards Organization – Rockwell Hardness Test Part 1 – Test Method (ISO 6508-1 Metallic Materials) The reason all steel product manufacturers use the Rockwell hardness scale is that it allows uniformity in reporting test results. Everyone in the steel industry recognizes the Rockwell hardness scale.
Rockwell Hardness Testing: Measures the permanent depth of indentation; Brinell Hardness Testing: Involves applying a known load to the surface of the test sample via a hardened steel or carbide ball; Vickers Hardness Testing: Utilises an optical measuring system to measure the area of the impression Once you have this information, you can use the following steps to calculate the Rockwell hardness value: Determine the Rockwell scale: The Rockwell scale is determined by the load applied and the type of indenter used. For example, the Rockwell C scale uses a 150 kgf load and a diamond cone indenter.There are two types of Rockwell test (Table 23.1): Rockwell: the minor load is 10 kgf, the major load is 60, 100, or 150 kgf. Superficial Rockwell: the minor load is 3 kgf and major loads are 15, 30, or 45 kgf. Table 23.1: Some common scales in Rockwell and Superficial Rockwell testing
C. When testing on the Rockwell B scale, if the HR value of an indentation exceeds 100 points, change the indenter ball. Make one indentation on a test block to seat the indenter and continue the measurement series on the specimen. If additional HR values in the test series exceed 100 points, a different scale will be used (e.g. Rockwell C scale).
For example, a ball approximately 10 mm in diameter is pressed into the surface of the material under an applied load commonly equal to 3,000 kgf for steels and 500 kgf for softer materials. The measurement of this indentation is done using an eyepiece micrometer microscope. . It covers various hardness testing scales (Rockwell, Vickers . The hardness reading represents the additional depth of penetration beyond the minor load. Tester accuracy is checked by running the test on specimens whose hardness has been certified by an independent testing laboratory. All Ames hardness testers perform genuine Rockwell Hardness tests, giving a direct Rockwell reading. Their accuracy meets .II. Theory and Principle of the Rockwell Hardness Test. The Rockwell Hardness Test uses a depth-differential method to test for hardness. A predetermined minor load is applied to the test sample, and the depth measurement is taken. Then a major load is applied to the same spot, which creates a deeper indentation.
main parts of polarimeter

Conforme já mencionado, a fusão renal ocorre quando uma parte de um rim está ligado ao outro rim. O rim em ferradura é a anomalia de fusão mais comum que existe, atingindo 1 em cada 500 crianças. No caso do rim em ferradura, além do defeito da migração de ambos os rins, ocorre a fusão de um ao outro. Os rins fundidos ficam ligados por .
the load appled in c-scale of rockwell hardness test is|rockwell hardness test distance